 |
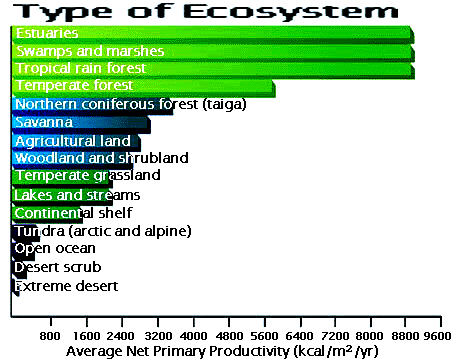
| Temperate Grasslands NPP (Dark Green) |
Gross Primary Productivity is the overall gain in energy/biomass per unit area per unit time which can be seen through photosynthesis or absorption by consumers. Basically it is what organisms actually do the photosynthesis and how much occurs and also how much biomass is produced.
Then Net Primary Productivity is the
total gain in energy or biomass per unit time by green plants after allowing
losses to respiration. This is used to see how much of the biomass is stored and then how much of it produces growth. The net productivity of the temperate grasslands
are around 2,200 kcal/m^2/yr.
 |
| Temperate Grassland Net Primary Productivity and how preoccupation effects it |
The productivity varies between the different
biomes and is highly dependent on how much light the biome get throughout the
year. This changes because the position of the earth relative to the sun
changes when it relieves around the sun. Thus making them more productive
around the equation because there is more light in that area and the plants can
do photosynthesis more of the year than in colder parts of the globe. The temperate grasslands are great for producing crops because of their temperature that is not to extreme for crops and they have an abundance of producers compared to there number of consumers in the biome.
In the Temperate Grasslands there are fires that occur because of the dryness of the
grasses and small amount of water. These fires make the trees that would be able to
grow to not be able to stay. This biome has two growing seasons, a growing
season and a dormant season where it is too cold and the grass cannot grow.
The plants in this biome are mostly shorter grasses some as short as a few
millimeters. These factors affect the productivity in the land and what kinds of plants can grow in the Temperate Grasslands.
The soil in the Grassland has become fertile from
the decomposition of organic matter from when the grasses die each year. Then
this rich soil is held in place by the deep roots of the perennial grasses. The fertile soil in most if the Temperate Grasslands are what help the plants grow and contribute the biome's productivity level. However, over time the grasslands soil has been used for just this purpose of growing large amounts of crops. This continual use and over use of the soil has made it, in some areas, very depleted. It needs to be taken care of in order to try to keep the soil rich and ideal for farming or animal substance.
The temperate grasslands used to be one of the
world's greatest ecosystems, because they have a moderate productivity, a diverse conglomeration of animals, and a climate that was beneficial to
most plant growth. However, of the world's 14 biomes the Temperate Grasslands are at the greatest risk because they have been the most altered
and least protected over time. Making the protection now even more important.
There are organization like The Temperate Grasslands Conservation Initiative
(TGCI) that agree that the grasslands are important and feel that they need to
be protected.
Addition Information Gathered
Form:
"IUCN, the International Union for
Conservation of Nature." IUCN. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Dec. 2014.
"Grasslands -- National
Geographic." National Geographic. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Dec.
2014.
"Taking Global Action: Towards a
Conservation Strategy for the World's Temperate Grasslands." Temperate
Grasslands Conservation Initiative4 (2010): n. pag. July 2010. Web. 11 Dec.
2014. <http://cmsdata.iucn.org/downloads/d3_july_2010_newsletter_4.pdf>.
No comments:
Post a Comment